Welcome to the Zhen Lab
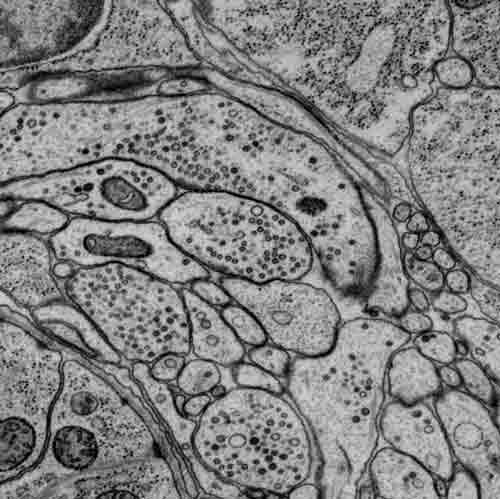
C. elegans is a compact model to study fundamental principles that govern circuit assembly and functions. We combine computational biology, electron microscopy, genetics, optogenetics, calcium imaging, and electrophysiology to address how its nervous system develops and operates. Insights obtained from our C. elegans and mouse studies to reveal circuit deficits that underlie human neurological disorders.
Resources
C. elegans wiring
nemanode.org
*NEW* 3D models of
C. elegans neurons
https://zenodo.org/record/5637219
https://zenodo.org/record/5525883
Codes (nemanodes)
https://github.com/dwitvliet/NemaNode
Original EM images
https://bossdb.org/project/witvliet2020
Plasmids
https://www.addgene.org/Mei_Zhen/
Other codes
https://github.com/zhenlab-ltri
Follow us on Twitter
Preprints & Recent Publications
Post-embryonic maturation of the C. elegans motor circuit Published, Current Biology
Connectomes across development reveal principles of brain maturation Published, Nature
Natural sensory context drives divers brain-wide activity during C. elegans mating Published, Cell
Corollary discharge promotes a sustained motor state in a neural circuit for navigation Published, eLife
Real-time volumetric reconstruction of biological dynamics with light-field microscopy and deep learning Published, Nature Methods
Structural analysis of the C. elegans dauer larval anterior sensilla by Focused Ion Beam-Scanning Electron Microscopy, Published, Frontiers In Neuroanatomy (Supplemental)
Extrasynaptic signaling enables an asymmetric juvenile motor circuit to produce a symmetric gait Published, Current Biology
Towards a live soft microrobot: optogenetic locomotion control of Caenorhabditis elegans Published, Science Robotics
Signal requirement for cortical potential of transplantable human neuroepithelial stem cells Published, Nature Communications
Escape Steering by Cholecystokinin Peptidergic Signaling Published, Cell Reports